
-
Short Run Production

-
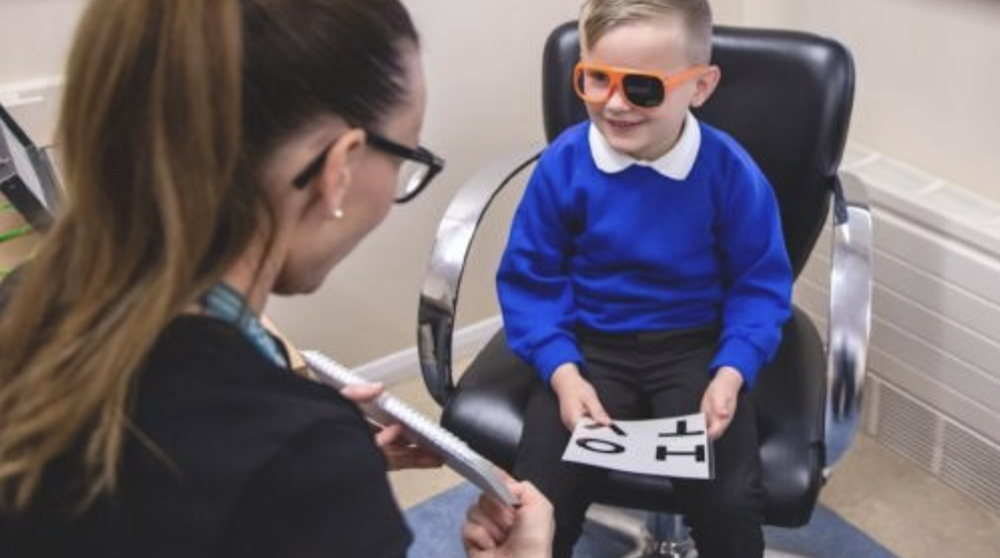
Clinical Trials Type
-
Personnel induction completed

-
6 Months Result Statistics

-
12 Months Reasult Statistics

-
18 Months Reasult Statistics
THEORY – PRACTICE – PATENT
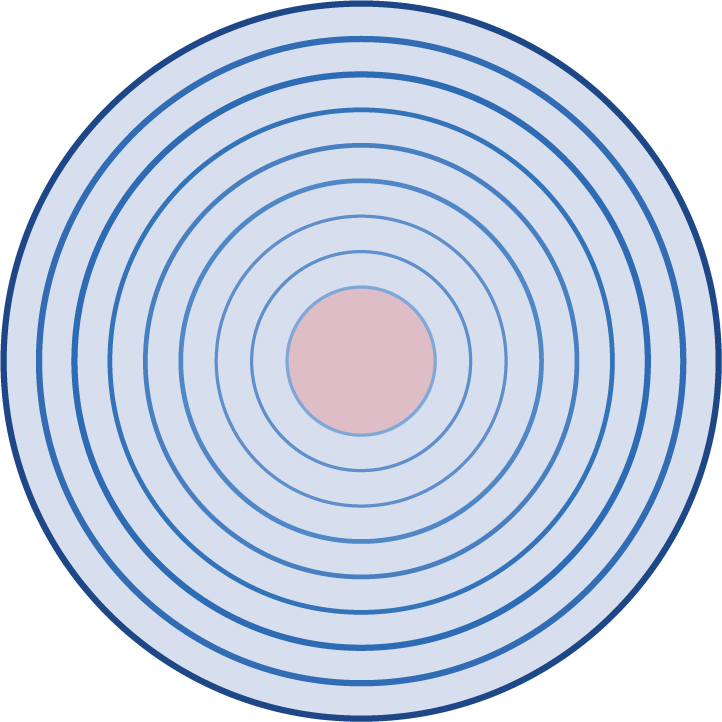
By performing corneal topographies of the eye after wearing orthokeratology lenses, they realized that corneal astigmatism was distributed in concentric circles.
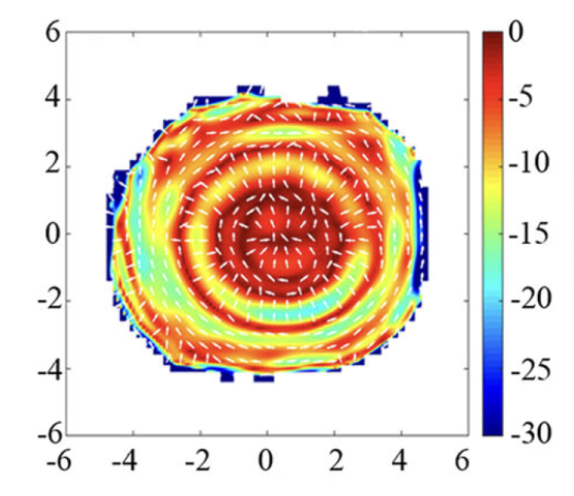
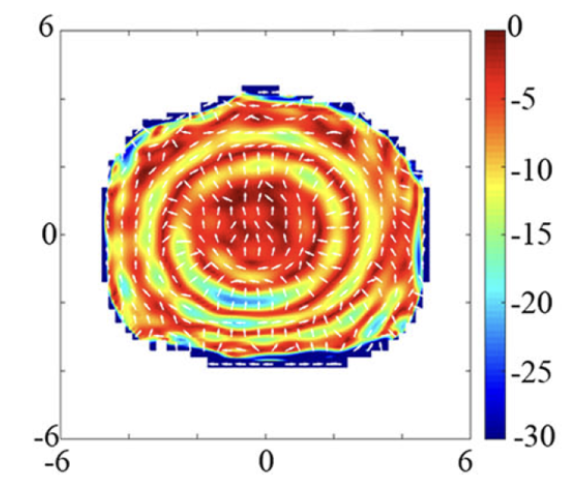
Corneal topographies after wearing an orthokeratology lens with representation of local surface astigmatism
It looks like a concentric wave on water

Concentric wave on water
Resulting lens MOOFX
Zone 1: central vision zone with far vision correction for the child
Zone 2: network of annular micro-cylinders evenly distributed between zone 1 and the edge of the lens to slow down myopia
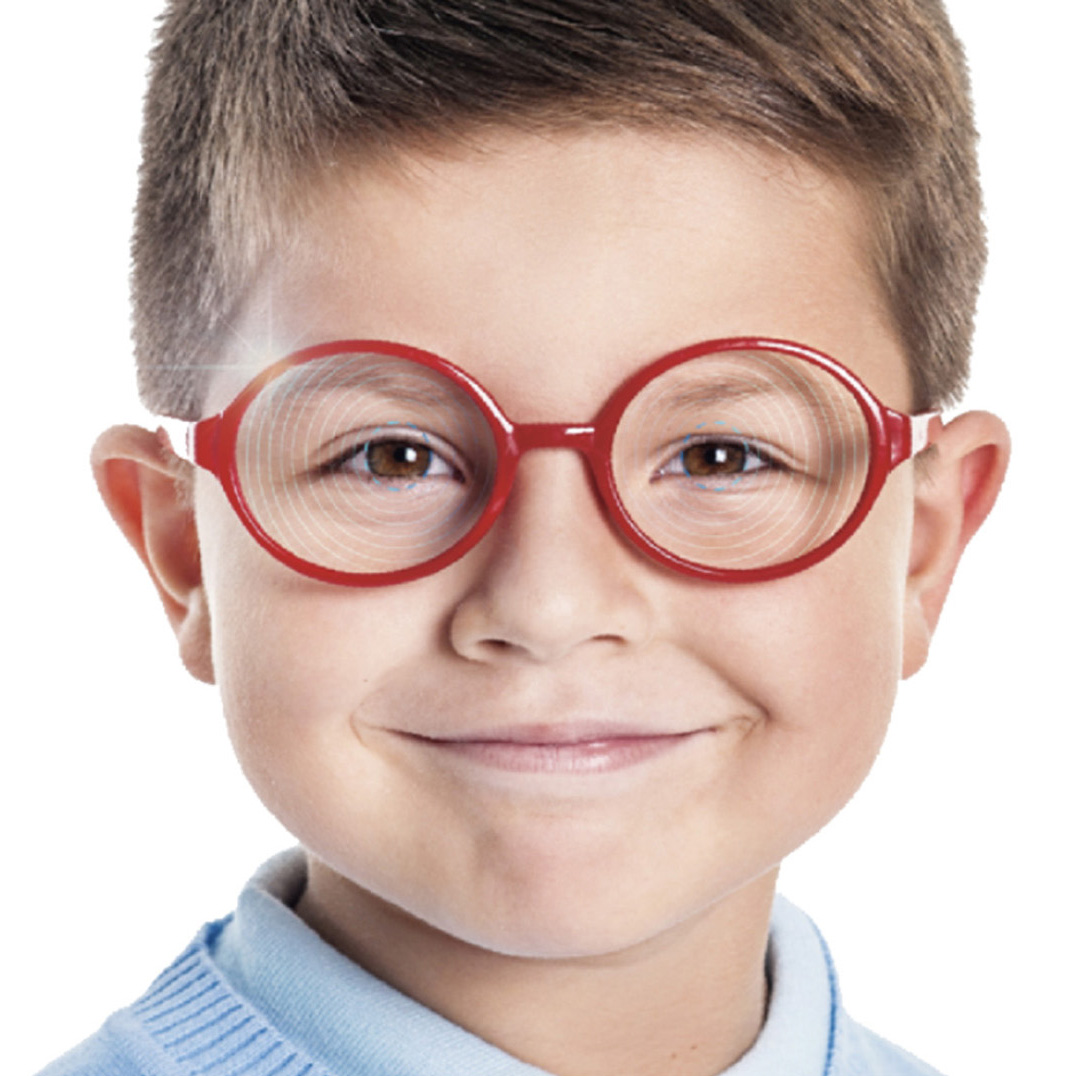
LENS EFFECT
MOOFX lens produces an effect of power Fluctuation Induced by Micro Cylinder Annular (F.I.M.C.A.). This power fluctuation will create high-order astigmatic aberrations on the retina and therefore alter the image perceived by the brain, which will have the effect of slowing down the progression of myopia. These cylindrical aberrations are said to be dynamic because they are oriented according to the meridian of the eye.
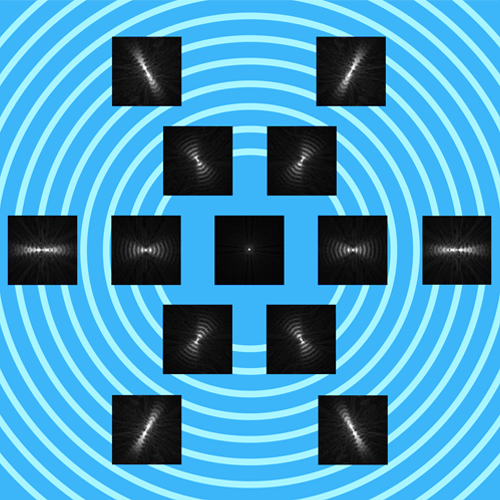
image of a light point through the MOOFX lens
CLINICAL STUDY
A clinical study of MOOFX has begun in august 2020 and is currently underway at Wenzhou University (China). The partial results (after 1 year) will be published shortly but we can already communicate them to you. A panel of 96 myopic children was divided into 2 groups, one equipped with MOOFX lenses, the other with classic single vision lenses (SVL).
Here are the characteristics of each group at the start of the study:
| MOOFX (n=52) | SVL (n=44) | P Value | |
| Age (years) | 10,1 ± 1,0 | 10,0 ± 1,1 | 0,58 |
| Male | 23 (44,2%) | 24 (54,5%) | |
| Female | 29 (55,8%) | 20 (45,5%) | |
| Cycloplegic SER (D) | -2,67 ±0,69 | -2,56 ±0,75 | 0,46 |
| Axial Length (mm) | 24,65 ±0,67 | 24,66 ±0,63 | 0,95 |
| Age of myopia onset (years) | 8,8 ±0,9 | 8,9 ±1,1 | 0,41 |
At 6-month intervals were measured:
- The cycloplegic Spherical Equivalent Refraction (SER)
- The Axial Length of the eye (AL)
SER and AL of each group at each control
SER(D):
| MOOFX (n=52) | SVL (n=44) | P Value | |
| Start | -2,67 ±0,69 | -2,56 ±0,75 | 0,46 |
| 6 months | -3,05 ±0,82 | -3,03 ±0,87 | 0,92 |
| 12 months | -3,25 ±0,83 | -3,27 ±0,88 | 0,84 |
AL(mm)
| MOOFX (n=52) | SVL (n=44) | P Value | |
| Start | 24,65 ±0,67 | 24,66 ±0,63 | 0,95 |
| 6 months | 24,84 ±0,71 | 24,88 ±0,66 | 0,77 |
| 12 months | 24,91 ±0,73 | 25,01 ±0,68 | 0,49 |
Curves of SER and AL values for each group
Mean changes in SER and AL in each group
SER(D):
| MOOFX (n=52) | SVL (n=44) | P Value | |
| Start to 6 months | -0,38 ±0,35 | -0,47 ±0,37 | 0,22 |
| 6 to 12 months | -0,19 ±0,26 | -0,24 ±0,31 | 0,36 |
| Start to 12 months | -0,56 ±0,46 | -0,71 ±0,39 | 0,1 |
AL(mm)
| MOOFX (n=52) | SVL (n=44) | P Value | |
| Start to 6 months | 0,19 ±0,12 | 0,23 ±0,12 | 0,18 |
| 6 to 12 months | 0,07 ±0,07 | 0,13 ±0,09 | 0,001** |
| Start to 12 months | 0,26 ±0,18 | 0,36 ±0,16 | 0,009* |
*P < 0,05 et **P < 0,025 indicate significant differences between the two groups
Curves of SER and AL values for each group
Since, we know also the results of variation of SER after 18 months and even if we do not have more details, we can draw the following curve:
Myopia Progression (SER)
CONCLUSION
We can therefore see that myopia effectively progresses more slowly in children equipped with MOOFX lenses than in others. Moreover, the fact that the two SER curves (MOOFX and SVL) tend to diverge more and more over time seems promising for the future.
It is also possible that our scientific team at the University of Wenzhou (China) decides to make changes to the lens (in the power, distribution and spacing of the annular micro-cylinders) to improve its efficiency.

For further information, please contact us:
VERBAL
15 rue du Sausset
93290 TREMBLAY-EN-FRANCE
www.verbal.fr
Email: info@verbal.fr